Appendix II: Using the
Barometer as an Altimeter
Set up Labpro:
Connect the barometer (which measures pressure) probe to the Lappro.† The settings arenít terribly important, but a setting of 10 sample/second with an over-sampling of 3 should be fine (and of course set the experiment length for a little over the time the balloon will be in the air).† Refer to Appendix II on how to set the Labpro for remote data taking.
How to get the height of the balloon from the pressure reading:†
Use the exponential formula for pressure vs. height, ![]() , where P is
the pressure reading at the height of interest, Po is the pressure at ground at sea level and equal to
101325 N/m2 = 2116 lb/ft2 = 14.69 lb/in2,
h is the height of the Pressure reading (i.e. height) and a = 8.42 km. -this
is the height the atmosphere would have to have if its density were constant with height, and equal to r0
(r0 = 1.225 kg/m3), in order to maintain pressure
Po at sea level.† So, one can use this formula, the pressure
reading P and the known value for
Po to find h.† Hereís
how itís done.† First decompose the
equation,
, where P is
the pressure reading at the height of interest, Po is the pressure at ground at sea level and equal to
101325 N/m2 = 2116 lb/ft2 = 14.69 lb/in2,
h is the height of the Pressure reading (i.e. height) and a = 8.42 km. -this
is the height the atmosphere would have to have if its density were constant with height, and equal to r0
(r0 = 1.225 kg/m3), in order to maintain pressure
Po at sea level.† So, one can use this formula, the pressure
reading P and the known value for
Po to find h.† Hereís
how itís done.† First decompose the
equation, ![]() †to solve for h.† This
is done by taking the natural log of† both sides of the equation and solving for h.
†to solve for h.† This
is done by taking the natural log of† both sides of the equation and solving for h.
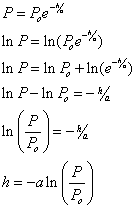
Example: ††Letís say you measure the pressure at the
ground to be 0.9841 atm (thus, Po=0.9841atm) and you measure the
pressure at a certain height to be 0.9724 atm (thus, P=0.9724 atm), in order to
find the height the balloon was at simply use the above equation, plugging in
the values.
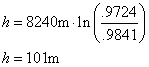 .†
.†
Note: if you want to find your height above sea level
(altitude), simply plug in 1.0 atm Po, this is the pressure at sea
level.
Accuracy:† The barometer is accurate to ![]() , which roughly corresponds to
, which roughly corresponds to ![]() accuracy in height; see below for a detailed check with
a range finder.
accuracy in height; see below for a detailed check with
a range finder.
One can also use the empirical model from NASA (this formula
is derived from fitting a function to data).†††
However, the exponential model only differs with the NASA empirical
model by ![]() †at 1000m altitude,
and even less for smaller altitudes.
†at 1000m altitude,
and even less for smaller altitudes.
At altitudes (see Glast website, classroom resources tab)† below 11km, here are the following fits for the atmosphere.
T = T0 (1 Ė h / 44329 m)
r = r0 (1 Ė h / 44329 m) 4.255876
P = P0 (1 Ė h / 44329 m) 5.255876