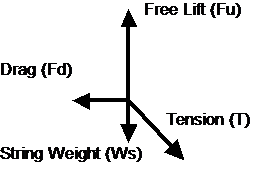Balloon Flight Analysis
Weight
Meteorological Balloons
|
Balloon Type |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Scientific Sales model # |
- |
8237 |
8244 |
|
Edmund Scientific order # |
30665-68 |
- |
- |
|
Cost |
$19 |
? |
$72 |
|
Nominal Inflation diameter |
4 ft |
5 ft |
6.3 ft |
|
Volume |
33 ft3 |
65 ft3 |
130 ft3 |
|
Bursting Inflation diameter |
8 ft |
13 ft |
30 ft |
|
Volume |
270 ft3 |
1100 ft3 |
14,000 ft3 |
|
Mass of Balloon |
110 g |
300 g |
1200 g |
|
Weight of Balloon |
1 N |
3 N |
12 N |
Lift of Helium in std. air = 32 g/ft3 = 0.31 N/ft3 = 11 N/m3 of vol.
A common 4 ft cylinder of helium contains 244 ft3 at 2490 psig and 70° F. This implies that the cylinder has a volume of 1.43 ft3.
Assuming constant temperature: PV = constant
![]()
Every 10 ft3 will use up about 103 psi for this size cylinder.
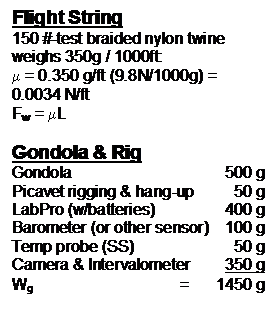
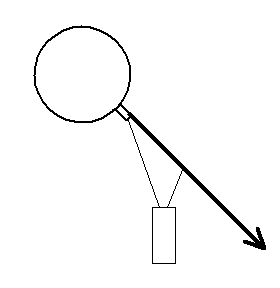
Forces
Free Lift
Fu = Lift due to Helium less weight of balloon & gondola
Fu = 31.7 g/ ft3 ·V – W = k2 r3 – W
k2 = 133 g/ft3 = 1.3 N/ft3
W1 = Wb + Wg = 110g + 1450g = 1560 g = 15 N
W2 = Wb + Wg = 300g + 1450g = 1750 g = 17 N
W3 = Wb + Wg = 1200g + 1450g = 2650 g = 26 N
In order to have a free lift of 500 g = 5 N at the ground:
r1 = 2.45 ft C=15.4 ft V=46 ft3 DP=473
psi
r2 = 2.53 ft C=15.9 ft V=51 ft3 DP=523
psi
r3 = 2.84 ft C=17.8 ft V=72 ft3 DP=739 psi
For every extra 100 g of payload, we will need an extra 3 ft3 of helium. For a std 4 ft cylinder this will require that DP=31 psi
Tension
T = tension in the flight string as a function of flight string length from the balloon.
Vertical component: Tv = Fu – Ws
Horizontal component: Th = Fd
Height

For a particular balloon, gondola, and 1000 ft of flight string, the altitude achieved will be determined by the ratio of the drag force and the net upward force. For a particular situation with a required weight to lift and a given wind speed, the only adjustable factor is the Free Lift which requires that we change the inflation radius.
Assumptions and
simplifications
Wind is moving uniformly with constant speed and direction and no turbulence.
Temperature is staying relatively constant and heating by sun is negligible.
The density of air remains constant over the entire range of altitude.
The string and gondola experience negligible drag.
The coefficient of drag is 0.5.
Flight Analysis
Using the above parameters, a mathematical model has been created (using Mathcad). From it the following guidelines have been estimated.
Balloon type 1
Minimum requirements for various Wind Speeds
Given: W = 15 N L = 1000 ft m = 350 g/1000 ft
with wind speeds: v = 1, 2, 5, &10 knots
In order the achieve at least 90% (900 ft) altitude we need the following:
|
Wind Speed |
Desc |
Free Lift at ground |
Inflation Radius |
Diameter |
Circumference |
|
1 knot |
Calm |
350 g |
2.43 ft |
4.86 ft |
15.3 ft |
|
2 knot |
Light Air |
375 g |
2.44 ft |
4.88 ft |
15.3 ft |
|
5 knots |
Light Breeze |
1.1 kg |
2.72 ft |
5.44 ft |
17.1 ft |
|
10 knots |
Gentle Breeze |
10 kg |
4.43 ft |
8.86 ft |
27.8 ft |
Maximum Altitudes and String Angles for various Wind Speeds
Given: Fu = 500 gm (Free Lift on the ground, ® r = 2.5 ft)
W = 15 N L = 1000 ft m = 350 g/1000 ft
with wind speeds: v = 1, 2, 5, &10 knots
|
Wind Speed |
Desc |
Maximum Altitude |
String Angle from Horiz. |
|
1 knot |
Calm |
999 ft |
85 ° |
|
2 knot |
Light Air |
979 ft |
70 ° |
|
5 knots |
Light Breeze |
647 ft |
24 ° |
|
10 knots |
Gentle Breeze |
218 ft |
6 ° |
General Guidelines
The balloon must be filled with helium until the balloon plus gondola has a net upward lift that is at least equal to the weight of 1000 ft of string (375 g).
In order to keep the maximum altitude within 10% (i.e. > 900 ft); for every knot of windspeed above 2 knots the balloon should have at least another 4 N (400 g) of net lift.
Increasing the radius by 10% will increase the free lift by about 60% of the total weight.
Appendix A: Wind Speeds
|
Knots |
Beaufort Number |
Name |
Effects observed |
|
Under 1 |
0 |
Calm |
Calm; smoke rises vertically |
|
1-3 |
1 |
Light air |
Smoke drift indicates wind direction; vanes do not move. |
|
4-6 |
2 |
Light breeze |
Wind felt on face; leaves rustle; vanes begin to move. |
|
7-10 |
3 |
Gentle breeze |
Leaves, small twigs in constant motion; light flags extended. |
|
11-16 |
4 |
Moderate breeze |
Dust, leaves, and loose paper raised up; small branches move. |
|
17-21 |
5 |
Fresh breeze |
Small trees in leaf begin to sway. |
|
22-27 |
6 |
Strong breeze |
Larger branches of trees in motion; whistling heard in wires. |
|
28-33 |
7 |
Near Gale |
Whole trees in motion; resistance felt in walking against wind. |
|
34-40 |
8 |
Gale |
Twigs and small branches broken off trees; progress generally impeded. |
Bowditch, American Practical
Navigator,